04/10/ · Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTubeShow that f(x, y, z)=x^{2}y^{2}z^{2} is continuous at the origin Our Discord hit 10K members!Get an answer for 'Given z = ln(sqrt x^2 y^2), show that x dz/dx y dz/dy = 1 Calculus of several variables question ' and find homework help for other Math
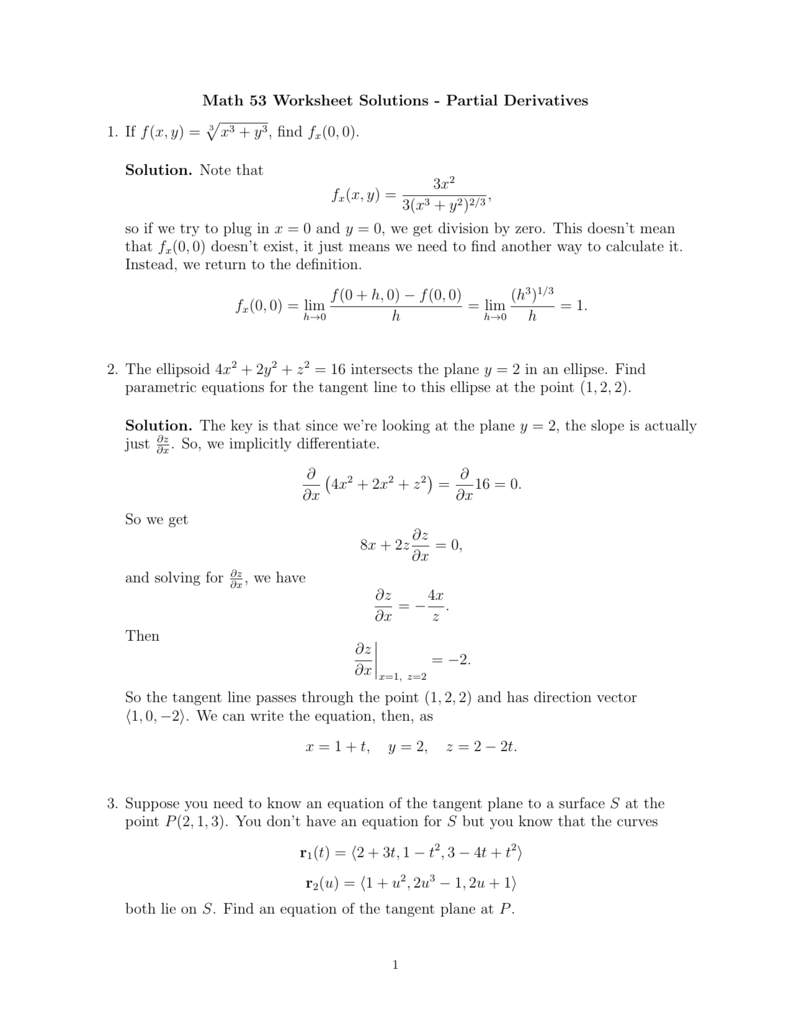
Math 53 Worksheet Solutions Partial Derivatives 1 If F X Y X3
If z=(x^(2)+y^(2))/(xy) show that x(del x)/(del x)+y(del z)/(del y)=0
If z=(x^(2)+y^(2))/(xy) show that x(del x)/(del x)+y(del z)/(del y)=0-To ask any doubt in Math download Doubtnut https//googl/s0kUoeQuestion If 2^x = 3^y =12^z show that 1/z= 1/y2/xIf xyz=0 then show that x^2/yxy^2/xzz^2/yx=3 cocplayeransh is waiting for your help Add your answer and earn points



Solved 2 Use The Divergence Theorem To Find The Outward Chegg Com
The plane that the x and z axes lie in) maThe paraboloid y = x z is shown in blue and orange The paraboloid x = y z is shown in cyan and purple In the image the paraboloids are seen to intersect along the z = 0 axis If the paraboloids are extended, they should also be seen to intersect along the lines z = 1, y = x;To ask Unlimited Maths doubts download Doubtnut from https//googl/9WZjCW If `xyyzzx=1` show that `x/(1x^2)y/(1y^2)z/(1z^2)=(4xyz)/((1x^2)(1y^2)(
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If x y z = 0 , show that x^3 y^3 z^3 = 3xyzShow tat 2 1 a n d 2 − 3 and the zeroes of the polynomial 4 x 2 4 x − 3 and also verify the relatiomship between the zeroes and the cooeficients of the polynomial View solution In the figure, the vertices of A B C are A ( 4 , 6 ) , B ( 1 , 5 ) and C ( 7 , 2 )Cones, just like spheres, can be easily defined in spherical coordinates The conversion from cartesian to to spherical coordinates is given below mathx=\rho sin\phi cos\theta/math mathy=\rho sin\phi sin\theta/math zmath=\rho cos\phi/m
Plot 1/(x^2 y^2) integrate x^2 y^2;18/04/21 · Consider the curved surface S defined by x 2 y 2 = z 2 for 0 ≤ z ≤ 1 (a) Make a sketch of the intersection of S with the x − z (ie, the y = 0) plane (remember to label your axes) (b) Express both the integrand and the surface element in spherical polar coordinates, and show that the surface integral Z x 2 x 2 y 2 dS over S has the value √π 2Any real function u(x, y) with continuous second partial derivatives which satisfies Laplace's equation, ∇2u(x, y) = 0 is called a harmonic function z(x, y) = ln(x2 y2) ∇2z(x, y) = ∂2z ∂x2 ∂2z ∂y2 you can solve the above expression and it must equal to 0 to be satisfied for the harmonic function Share answered Mar 28 '16 at 642



Factorise I 2 X 3 3 X 2 17 X 30 21 If Both X 2 And Left X Frac 1 2 Right Are Factors Of P X 2 5 X R Show That P R 22 If Z 2 Frac 1 Z 2 14 Find The Value Of Z 3 Frac 1 Z 3



Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu
Show that $z = \ln (x^2y^2) 2\tan^{1}(y/x)$ satisfies the laplaces's equation17/04/21 · Solve for integers $x, y$ and $z$ $x^2 y^2 = z^3$ I tried manipulating by adding and subtracting $2xy$ , but it didn't give me any other information, except theIf U = F ( Y − X X Y , Z − X X Z ) , Show that X 2 ∂ U ∂ X Y 2 ∂ U ∂ Y Z 2 ∂ U ∂ Z = 0 Applied Mathematics 1 Sum If u =`f ( (yx)/ (xy), (zx)/ (xz)),` show that `x^2 (delu)/ (delx)y^2 (delu)/ (dely)z^2 (delu)/ (delz)=0` Advertisement Remove all ads



If X Y Z 9 And Xy Yz Zx 23 The Value Of X 3 Y 3 Z 3 3xyz Youtube



How To Solve The Ordinary Differential Equation X 2 Y 2 X Y 2y X 4 Mathrm E X Mathematics Stack Exchange
X = 2 − z 2 4 y z − 4 y 2 z x = 2 z 2 4 y z − 4 y 2 z , z ≤ − 2 2 ∣ y ∣ − 2 y or z ≥ 2 2 ∣ y ∣ − 2 y Steps Using the Quadratic Formula Steps for Completing the SquareShow that the $\max{ \{ x,y \} }= \dfrac{xyxy}{2}$ I do not understand how to go about completing this problem or even where to startNote that if ω is a complex cube root of unity, then x 2 y 2 z 2 − x y − y z − z x = (x y ω z ω 2) (x y ω 2 z ω) Thus it is sufficient to prove that x y ω z ω 2 Find the equation, center, foci, and the lengths of the major & minor axes from \displaystyle{x}^{{2}}{2}{y}^{{2}}{12}{y}{4}{x}{2}={0} ?



Use A Chain Rule To Find The Values Of Left Frac Partial Z Partial R Right R 2 Theta Pi 6



If Sin X Y P Sqrt 1 P 2 And Cos X Y 1 Sqrt 1 Q 2 Then Sh
It looks like treating each variable separately makes you overestimate the bound If you use MVT for f as a function of two variables, you have f(x_1,y_1)f(x_2,y_2)=\nabla f(\vec{p}) \cdot \big( (x_1,y_1)(x_2,y_2)\big)15/03/07 · (x y)^2 = x^2 2xy y^2 Earlier, when I put x^2 2xy y^2 is the bracket, I meant to keep it away from z^2 so that the factoring would be clearer for you Sorry I confused you instead I think what you didn't get was the x^2 and y^2 in the bracket and the appearence of (x y)^2 in the next step (x^2 y^2) = (x y)^2 is a wrong/10/12 · The Attempt at a Solution I know that the way to do this is to substitute the Lorentz transformations into the original invariant and then do some algebra, but I end up with the following T ′ = c 2 ( Δ t ′) 2 − ( Δ x ′) 2 − ( Δ y ′) 2 − ( Δ z ′) 2



Prove That 2 Y Z X Varies As Yz If Z X 2y X Y 2z Varies As Yz And Sum Of X Y Z Is Constant Youtube



Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download
09/10/19 · If x, y, z are different and Δ = (x, x2, 1 x3), (y, y2, 1 y3), (z, z2, 1 z3) = 0 then show that 1 xyz = 0 We have Now, we know that If some or all elements of a row or column of a determinant are expressed as sum of two (or more) terms, then the determinant can be expressed as sum of two (or more) determinantsCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history, geography, engineering, mathematics, linguistics, sports, finance, music WolframAlpha brings expertlevel knowledge andAs an example let's show xyz is divisible by 4 by case analysis 1) Suppose z=0 (mod 4) Then xyz=0 (4) trivially 2) Suppose z=1 (4) Then z^2=1 (4) so x^2y^2=1 (4) Hence one of x or y must be 0 (4) while the other must be 1 (4) It follows xyz=0 (4) 3) Suppose z=2 (4) Then z



Evaluate Please X 2 Y 2 3 Y 2 Z 2 3 Z 2 X 2 3 Divided By X Y 3 Y Z 3 Z X 3 Brainly In


Solved Find The Volume Of The Given Solidunder The Surfac Chegg Com
Show that {eq}x^2 y^2 z^2 4x 6y 2z 6 = 0 {/eq} is the equation of a sphere, and find its center and radius Equation for a Sphere Equations for spheres are very similar to equation ofTranslate Edited Stephan on 14 Sep 18 Hi, use syms x y f (x,y) = x^2 y^2;Get an answer for 'Show that z=ln((x^2) (y^2)) is a solution of Laplace's equation δ^2z/δx^2 δ^2/δy^2 = 0' and find homework help for other Math questions at eNotes


If Z X Y X 2 Y 2 Show That Delz Delx Delz Dely 2 4 1 Delz Delx Del Youtube



Y Xy 3 1 X 2 1 2 Y 0 1 Harushley
Have a question about using WolframAlpha?23/06/15 · Suppose f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 and W is the solid cylinder?06/12/12 · Show that x^2 y^2 z^2 4x 6y 2z 6 = 0 is an equation of a sphere find its centre and radius?



Ex 9 2 6 Verify Y X Sin X Xy Y X Root X2 Y2



If X At 2 Y 2at Then D 2y Dx 2 Is Equal To Youtube
Show that the function f(x, y, z) = (x 2 y 2 z 2 ) −1/2 satisfies Laplace's partial differential equation ∂ 2f ∂x2 ∂ 2f ∂z2 ∂ 2f ∂y2 = 0 Expert Answer Previous question Next questionIn this section we show the follo wing result which characterizes the solution of the diophantine equation x 2 3 y 2 = z 2 Proposition 21 If ( x, y, z) ∈ Z 3 is a solution of the17/11/ · Ex 25, 13 If x y z = 0, show that x3 y3 z3 = 3xyz We know that x3 y3 z3 3xyz = (x y z) (x2 y2 z2 xy yz zx) Putting x y z = 0, x3 y3 z3 3xyz = (0) (x2 y2 z2 xy yz zx) x3 y3 z3 3xyz = 0 x3 y3 z3 = 3xyz Hence pro



Answered Homework 2 Q1 Find The Second Partial Bartleby



Math 53 Worksheet Solutions Partial Derivatives 1 If F X Y X3
Show that the differential equation d x d y (3 x 4 y 5) − (2 x 3 y 4) d x d y = 0 into homogeneous equation, origin is shifted to (h, k) then h k = Medium View solution If u = lo g (x 2 y 2 z 2), verifyX 2 y 2 = z Subtract x^ {2} from both sides Subtract x 2 from both sides y^ {2}=zx^ {2} y 2 = z − x 2 Take the square root of both sides of the equation Take the square root of both sides of the equation y=\sqrt {zx^ {2}} y=\sqrt {zx^ {2}} y = z − x 2 y = − z − x 2If Y is the Mean Proportional Between X and Z Prove that (X^2 Y^2 Z^2)/(X^(2) Y^(2) Z^(2)) = Y^4 Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion (Including



X3 Y3 Z3 3xyz X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 Xy Yz Zx Proof It Lhs To Rhs Brainly In



Show That Z Ln X 2 Y 2 2 Tan 1 Y X Satisfies The Laplaces S Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange
We have x^2y^2=36z^2 and xy=10z, which gives (10z)^22xy=36z^2 or xy=3210zz^2 and xyz=32z10z^2z^3 Also, (xy)^2\geq4xy, which gives 3z^2z28\leq0 or 2\leq z\leq\frac {14} {3} We have x2 y2 = 36−z2 and x y = 10−z, which gives (10−z)2 −2xy = 36−z2 or xy = 32− 10z z2 and xyz = 32z − 10z2 z3With height 9 and base radius 2 that is centered about the zaxis with its base at z=2 Answer Save 1 Answer Relevance kb Lv 7 6 years ago Favorite Answer The cylinder has equation x^2 y^2 = 2^2, which can be rewritten as r = 2 in cylindrical coordinates As you stated, z is inFsurf (f, 4 4 4 4) Note that this will work if you have access to th Symbolic Math Toolbox If you dont have it, the answer from KSSV will always work



Line Integral Example 1 Video Khan Academy



If X Y Z 6 And Xy Yz Zx 11 And Xyz 6 Is Given Find The Value Of X 3 Y 3 Z 3 Youtube
Series x^2 y^2;22/01/ · Ex 42, 9 By using properties of determinants, show that 8(x&x2&yz@y&y2&zx@z&z2&xy) = (x – y) (y – z) (z – x)(xy yz zx) Solving LHS 8(𝑥&𝑥^2&𝑦𝑧@𝑦&𝑦^2&𝑧𝑥@𝑧&𝑧^2&𝑥𝑦) Applying R1→ R1 – R2 = 8(𝑥−𝑦&𝑥^2−𝑦^2&𝑦𝑧−𝑥𝑧@𝑦&𝑦^2&𝑧𝑥@𝑧&𝑧^2&𝑥𝑦) Ex 42, 9 By using properties of determinants, sClick here👆to get an answer to your question ️ Show that x^2 xy y^2, z^2 zx x^2 and y^2 yz z^2 are consecutive terms of an AP, if x, y and z are in AP



If U F R Where R 2 X 2 Y 2 Then 2u X 2 2u Y 2


Find The Product X Y Z X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Xy Yz Zx Youtube
Z = −1, y = −xAnswer (x^2 4x 4) (y^2 6y 9) (z^2 2z 1) = 6 4 9 1> (x2)^2 (y3)^2 (z1)^2 = 8 for the first line, I dont get the connection ofInvert colors image of x^2 y^2;
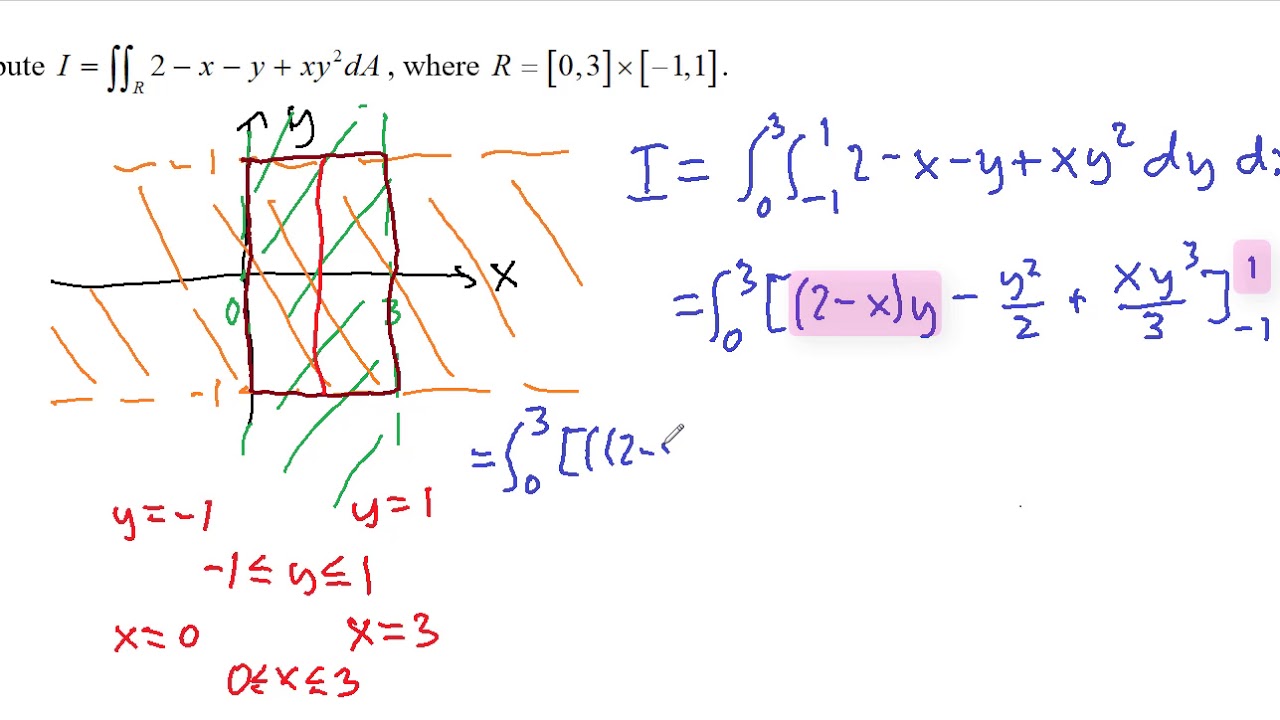


Double Integrals Volume And Average Value


14 2 Limits And Continuity
Contour plot Download Page POWERED BY THE WOLFRAM LANGUAGE Related Queries x^2 y^2 vs differentiate x^2 y^2;For the xzplane set y equal to zero This gives you the curve (trace) where that plane cuts through your surface What you have left will describe a curve in the y=0 plane (also known as the xz plane;🎉 Meet students and ask top educators your questions



Hw 10 New 1



Solved Find All Second Order Partial Derivatives For The Chegg Com
30/08/ · Can't, because your math language is incorrect Learn PEDMAS computers demand correctness z^(1/2) is what you (seem) to mean You can also say z^5 As I simplify the equations, you want us to show that 0 = 4xy (only possible if x and/or y = 0)/07/14 · Show that the function f(z)=e^(x^2y^2)cos(2xy)isin(2xy) is entire, and find its derivativeShow that {eq}f(x,y,z) = (x^2 y^2 z^2)^{\frac{1}{2}} {/eq} satisfies the Laplace equation {eq}\frac{\delta^2f}{\delta x^2} \frac{\delta^2f}{\delta y^2} \frac{\delta^2f}{\delta z^2} = 0 {/eq}



Contour Map Of F X Y 1 X 2 Y 2 Youtube



If X 4 9 Y 7 12 And Z 2 3 Then Verify That X Y Z Not Equals X Y Z Brainly In
11/11/18 · Using properties of determinants, prove the following (x,y,z),(x^2,y^2,z^2),(x^3,y^3,z^3)=xyz(xy)(yz)(zx) asked May 8, 18 in Mathematics by rubby ( 518k points) determinantIf zw ne 0, then (x,y) notin {(1, 1), (7/5,1/5)} For eliminating z, 2 1 = x^2 y^2 w^2 x 2y 3w^2 2w^2 = x^2 y^2 x 2y 3 For eliminating w, 3 * 2 1 = 3x^2 3y^2 3z^2 x 2y z^2 2z^2 = 3x^2 3y^2 x 2y 7 So, we got ((w^2),(z^2)) = 1/2 ((f_1(x,y)), (f_2(x,y))) And you don't want that f_1 = f_2 = 0 For eliminating x^2, 3f_1 f_2 = 0 Rightarrow 3x x 6y 2yShow that $\\(x,y,z)\\ = x 2 \\sqrt{y^{2} z^{2}}$ is a norm on $\\mathbb{R}^3$ My issue comes with showing the 3rd condition, ie the triangle inequality After some expansion I
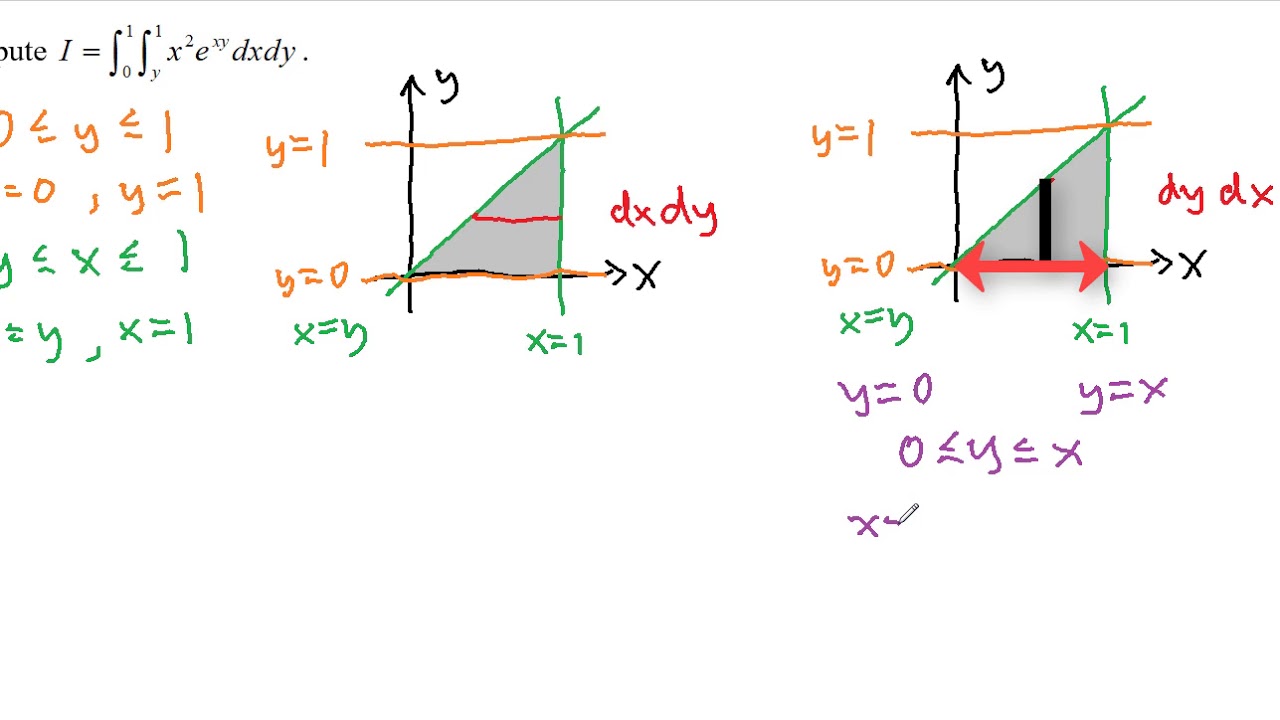


Double Integrals Volume And Average Value
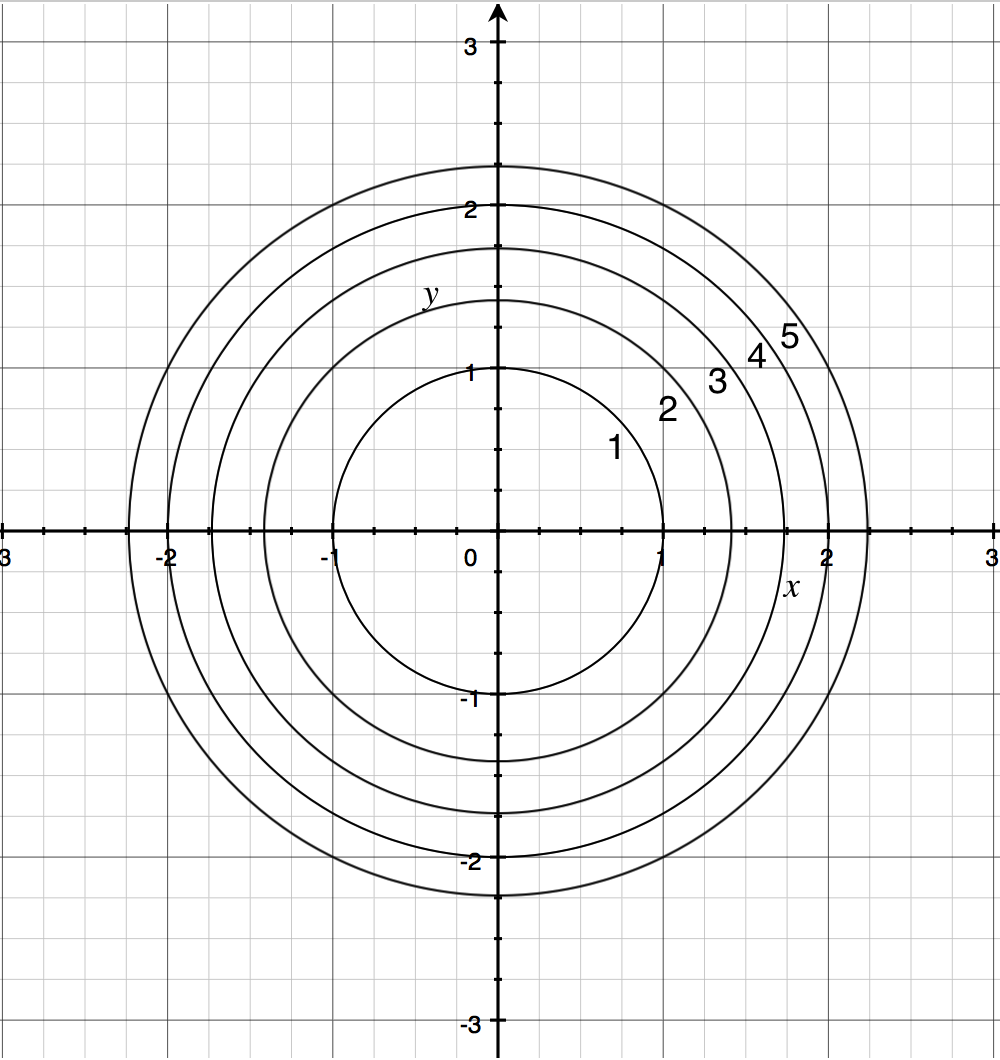


Contour Maps Article Khan Academy
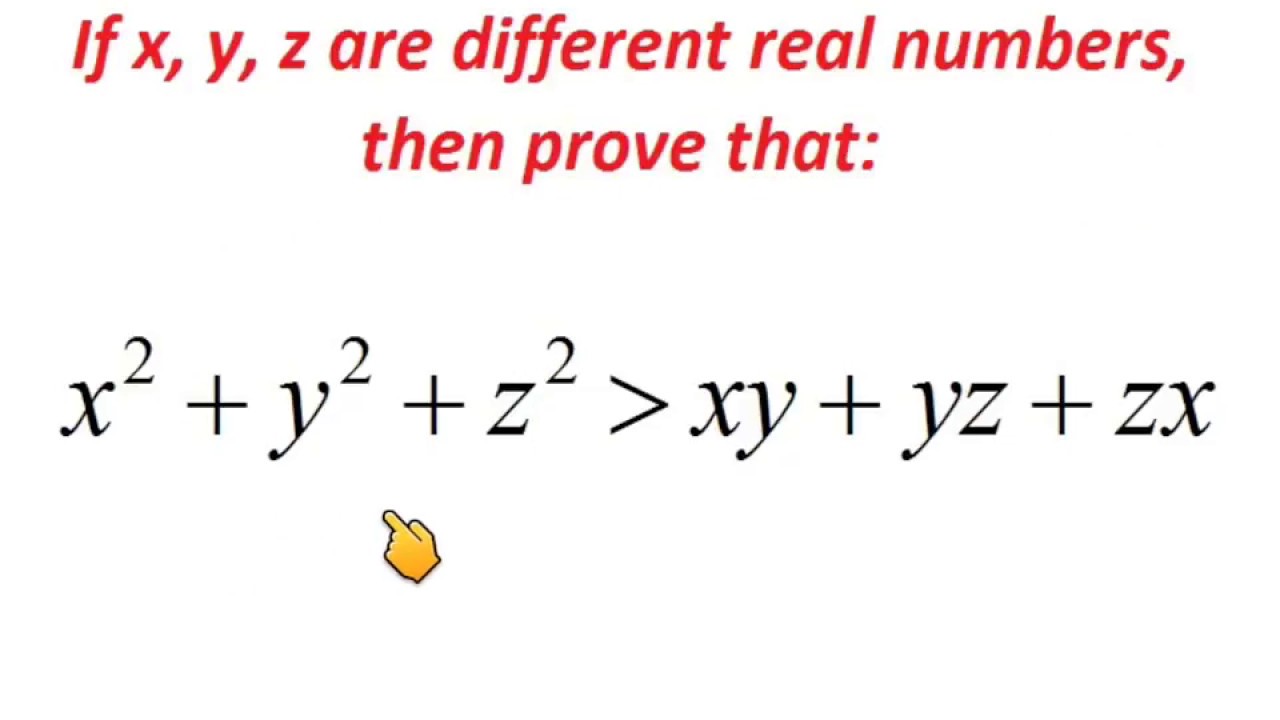


X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Greater Than Xy Yz Xz Proof Important For Iit Jee Nda Scra Sat Competitive Exams Youtube



Solved Consider The Function F That Is Given By F X Y Chegg Com



Solved 2 Use The Divergence Theorem To Find The Outward Chegg Com



Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download
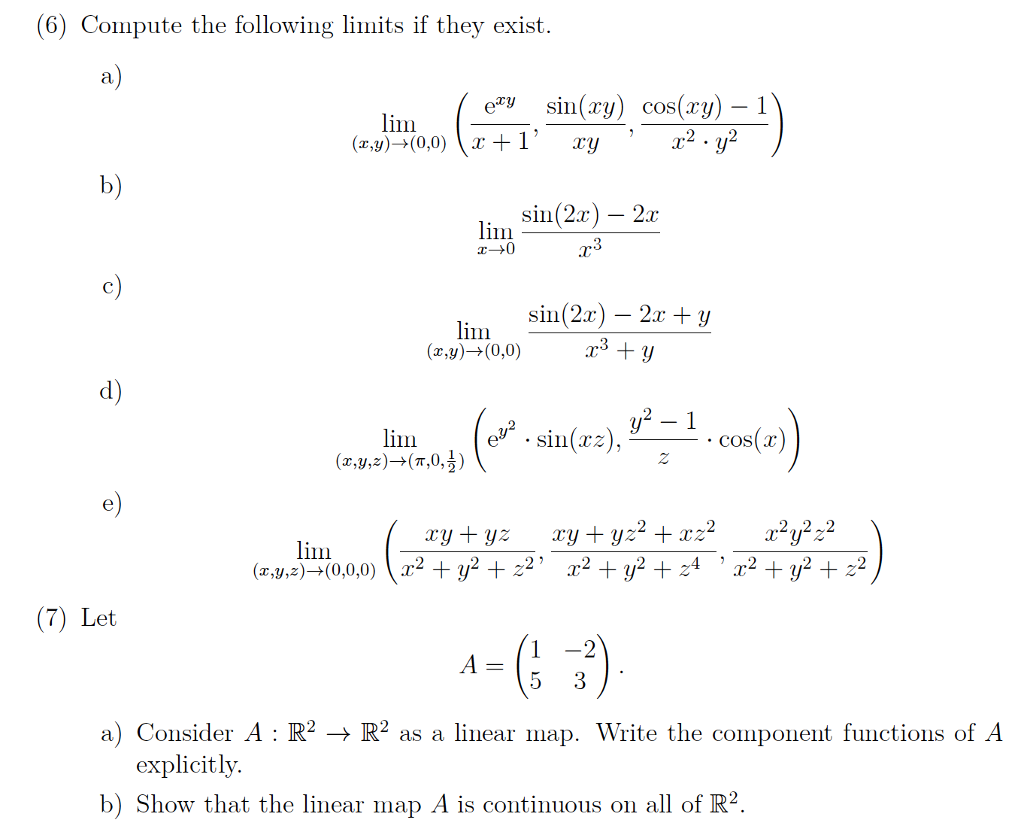


Solved 6 Compute The Following Limits If They Exist Ii Chegg Com



If X Y Z Are In Ap Then Find The Value Of X 2y Z 2y Z X Z X Y Brainly In



2 Partial Differentiation



Solved If Z Xy X Ey X Show That X Z X Y Z Y Xy Chegg Com



Exercises S1 4



Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu



Solved Please Try And Answer All Of Them Show All Work Chegg Com



Solved Evaluate Xy Y Z Ds Along The Curve R T 2t I Chegg Com



Exact Equations Example 1 Video Khan Academy



Solved Evaluate The Limits Or Show That That Do Not Exist Chegg Com



Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu


Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download



If 3 X 5 Y 75 Z Show That Z Xy 2x Y Brainly In
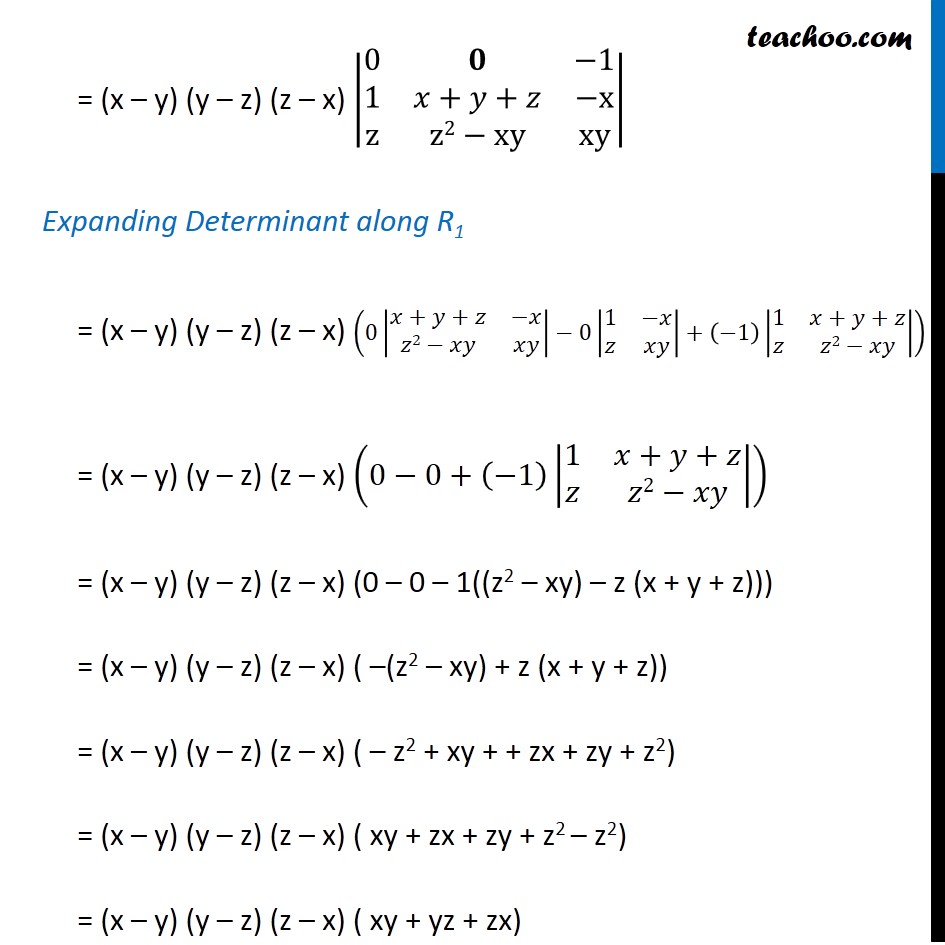


Ex 4 2 9 Show That X X2 Yz Y Y2 Zx Z Z2 Xy X Y Y Z


What Is The Solution Of Differential Equation D 2y Dx 2 2 Dy Dx Y 0 When X 0 Y 1 Dy Dx 2 Quora



If X Y Z 0 Then Prove That X 2 Yz Y 2 Zx Z 2 Xy 3 Brainly In
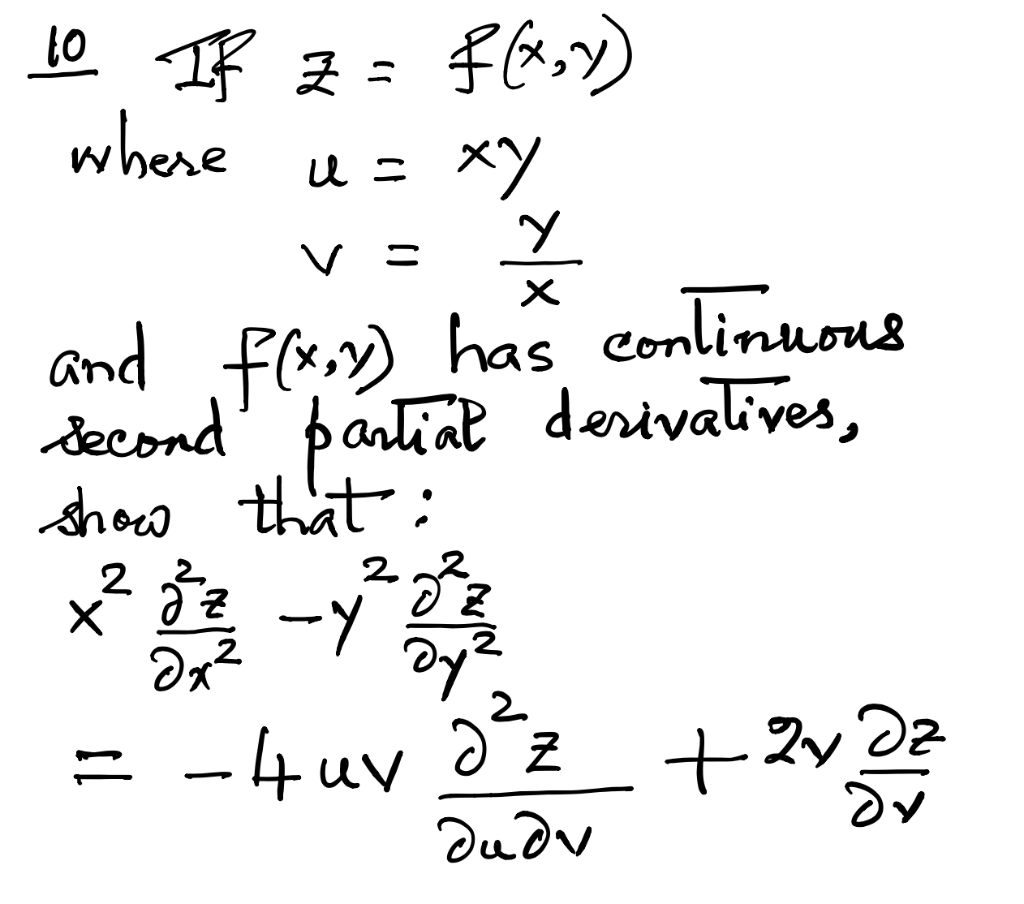


Solved 10 If Z Where F X Y U Xy V U H And F X Y Has Chegg Com
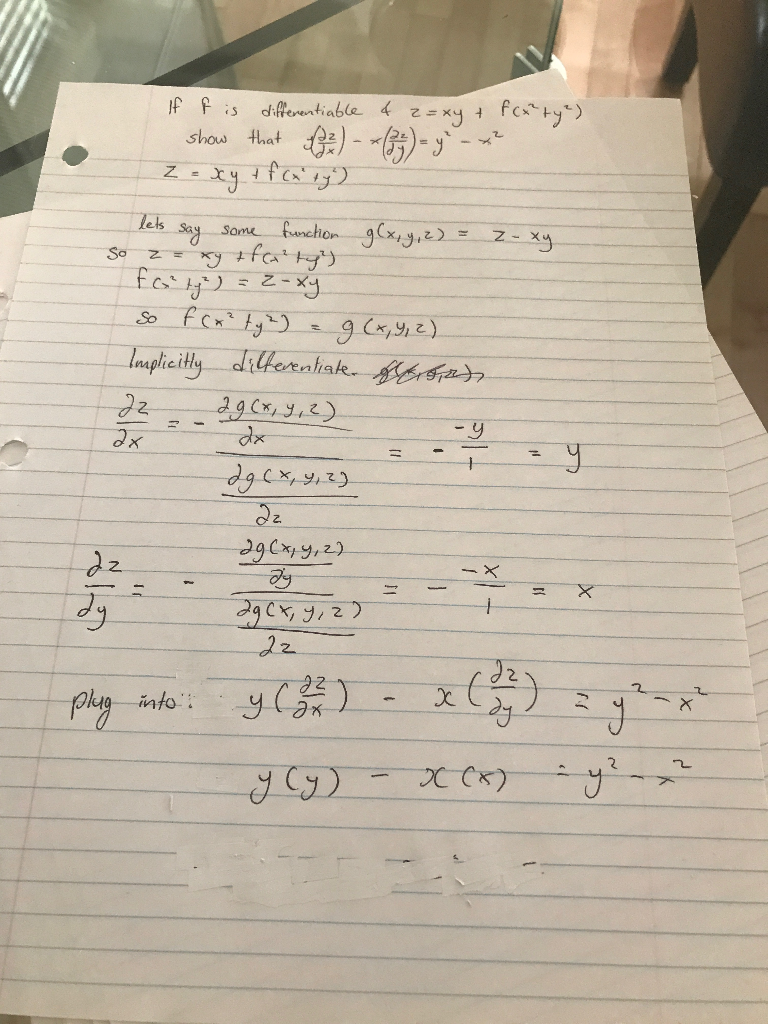


Solved If F Is Differentiable Z Xy F X 2 Y 2 Show That Chegg Com



How Can I Prove That Xy Leq X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
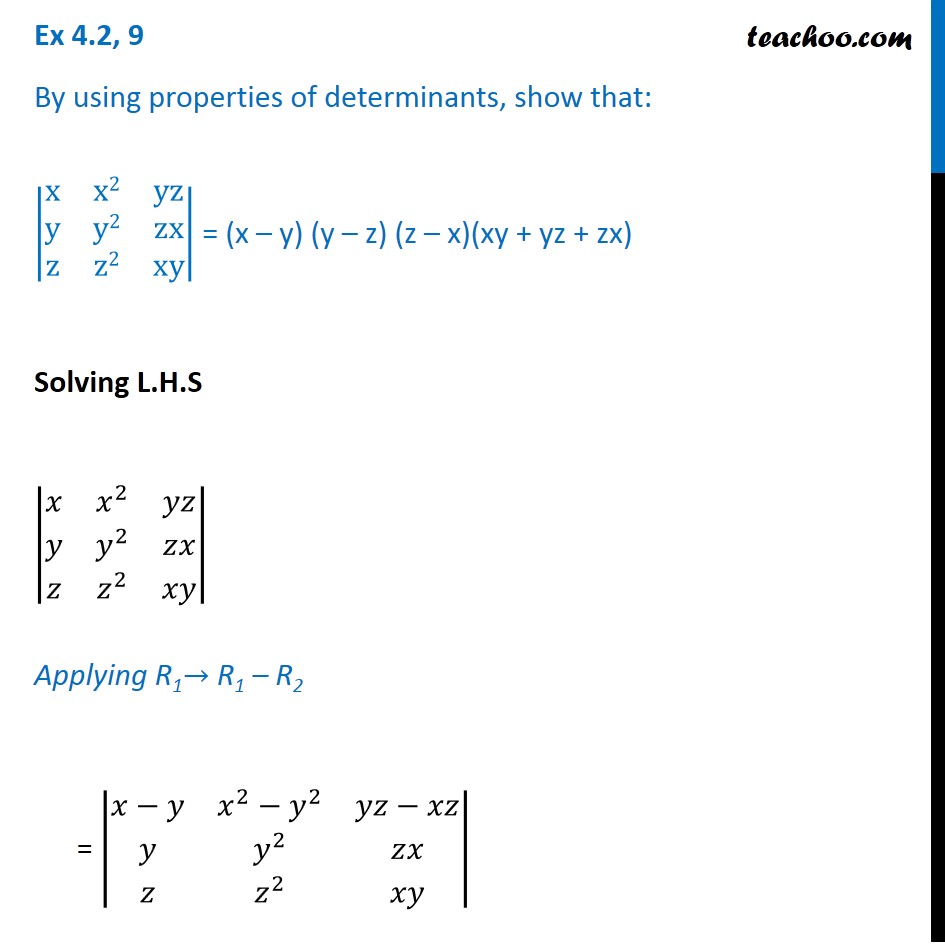


Ex 4 2 9 Show That X X2 Yz Y Y2 Zx Z Z2 Xy X Y Y Z



Tangent Plane To X 2 Xy Y 2 Z 0 Youtube
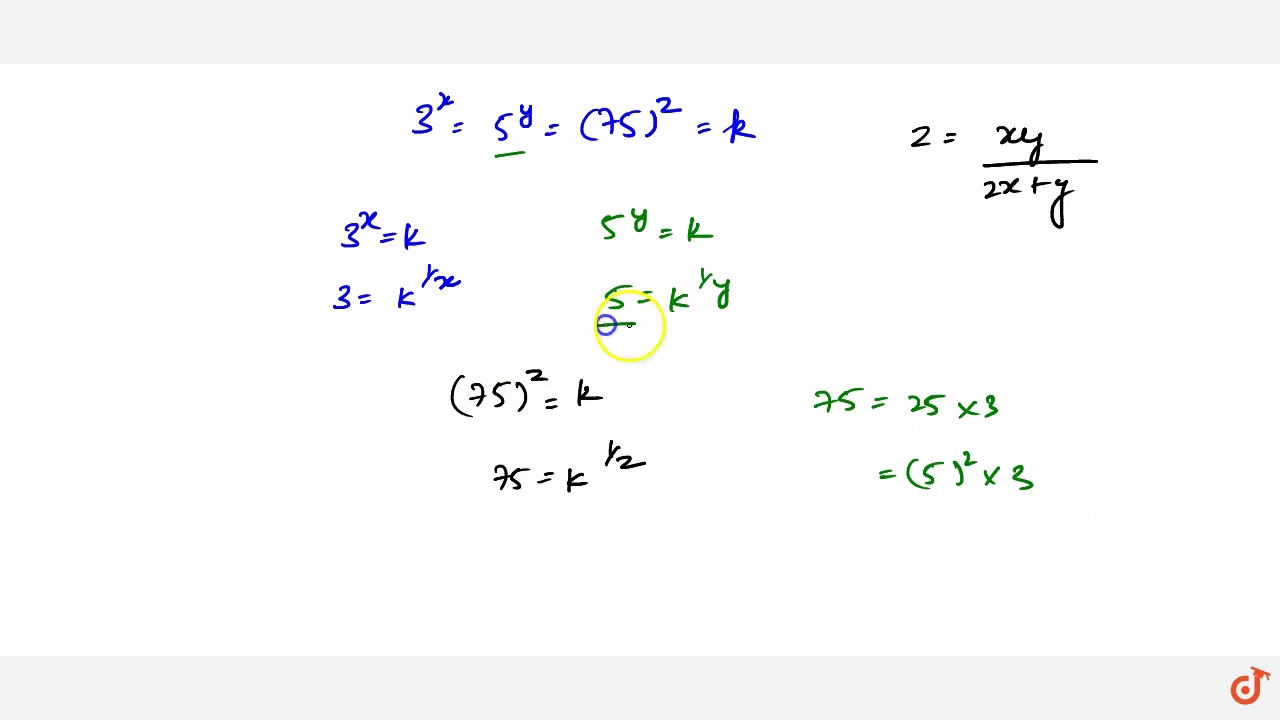


If 3 X 5 Y 75 Z Show That Z Xy 2x Y Youtube



Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu


What Is Xyz When Xyz Xyz Xyz Zzz Quora



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿